网络设备的初始化 :
包括2个阶段:
- 作为常规device,初始化
- 作为network device,初始化
|
|
Initialization Options:
Both components built into the kernel and components loaded as modules can be passed input parameters so that users can fine-tune the functionality implemented by the components, override defaults compiled into them, or change them from one system boot to the next, kernel provides two kinds of macros to define options:
- Module options module_param family
- Boot-time kernel options _ _setup family
drivers/block/loop.c
Module options.
module_param
The module parameters are listed in the module’s directory “/sys/modules”. The subdirectory /sys/modules/module/parameters holds a file for each parameter exported by module.
Initializing the Device Handling Layer: net_dev_init
|
|
subsys_initcall(net_dev_init);
subsys_initcall macros ensure net_dev_init runs before any NIC device drivers register themselves.
main parts of net_dev_init:
/proc/net is created by net_dev_init, via dev_proc_init and dev_mcast_init:
User-Space 工具
/sbin/modprobe
Invoke when the kernel needs to load a module./sbin/hotplug
Invoke when the kernel detects that a new device has been plugged or unplugged from system.
The kernel provides a function named call_usermodehelper to execute such user-space helper.
Two kernel routines, request_module and kobject_hotplug , invoke call_usermodehelper to invoke /sbin/modprobe and /sbin/hotplug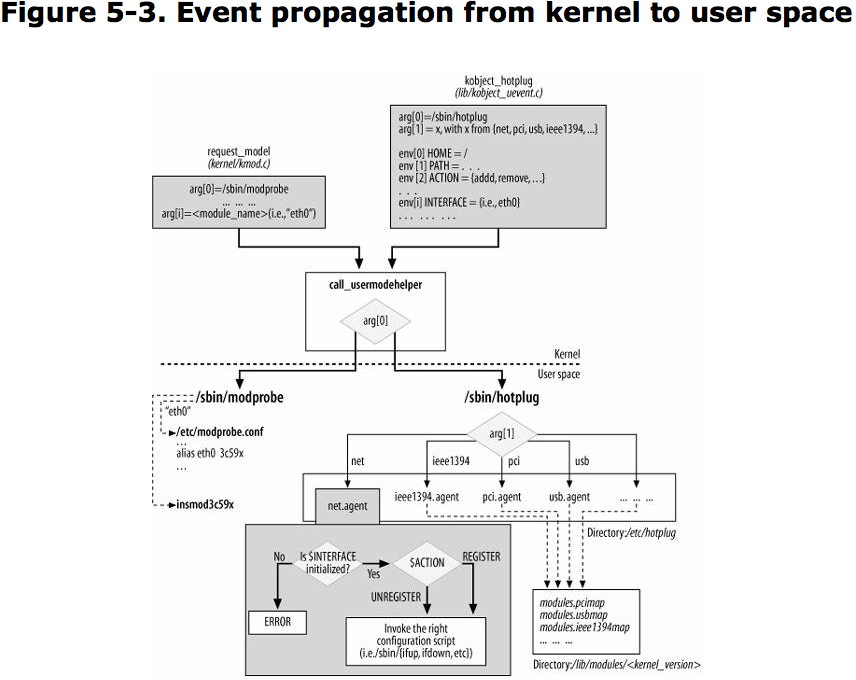
kmod is the kernel module loader that allows kernel components to request the loading of module. call request_module
Hotplug was introduced into the kernel to implement popular consuer feature known as Plug and Play (PnP). When compile the kernel modules, the object files are placed by default in directory: /lib/modules/kernel_version/. kobject_hotplug function is invoked by the kernel to respond to insertion and removal of a device.
modprobe and hotplug create file/directory in /proc/sys/kernel
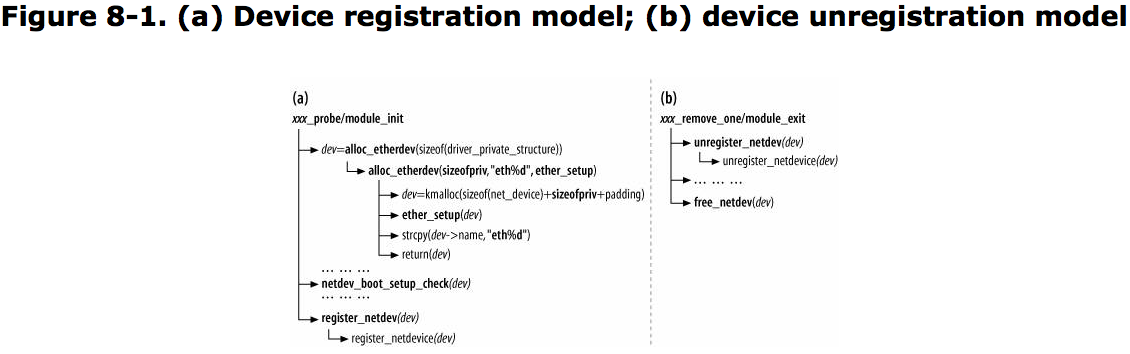
When a Device is Registered:
The registration of a network device takes place in the following situations:
- Loading an NIC’s device driver
- Inserting a hot-pluggable network device
When a Device is Unregistered:
Two main conditions trigger the unregisteration of a device:
- Unloading an NIC device driver
- Removing a hot-pluggable network device
Allocating net_device Structures:
Network devices are defined with net_device structures.
include 3 input parameters:
- Size of private data structure
- Device name
- Setup routine
Device Initialization:
net_device structure is pretty bug, its fields are initialized in chunks by different routines.
- Device drivers : Parameters such as IRQ, I/O memory, and I/O port, those values depend on hardware configuration, are taken care of by device driver. xxx_probe
- Device type : the type family is taken care by xxx_setup routines.
- Features: Mandatory and optional features also need to be initialized.
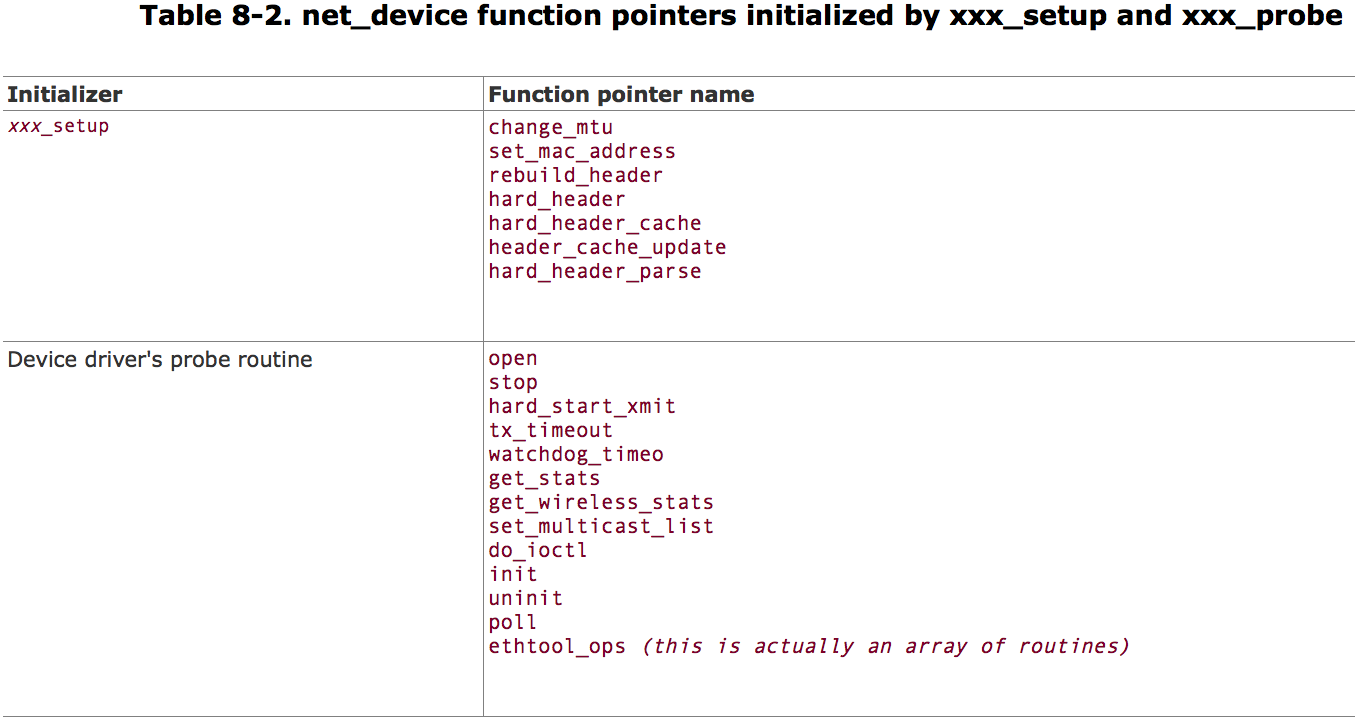
Device Type Initialization: xxx_setup Functions
alloc_ xxxdev function pass right xxx_setup routine to alloc_netdev .
void ether_setup(struct net_device *dev)
{
dev->change_mtu = eth_change_mtu;
dev->hard_header = eth_header;
dev->rebuild_header = eth_rebuild_header;
dev->set_mac_address = eth_mac_addr;
dev->hard_header_cache = eth_header_cache;
dev->header_cache_update = eth_header_cache_update;
dev->hard_header_parse = eth_header_parse;
dev->type = ARPHRD_ETHER;
dev->hard_header_len = ETH_HLEN;
dev->mtu = 1500;
dev->addr_len = ETH_ALEN;
dev->tx_queue_len = 1000;
dev->flags = IFF_BROADCAST|IFF_MULTICAST;
memset(dev->broadcast,0xFF, ETH_ALEN);
}
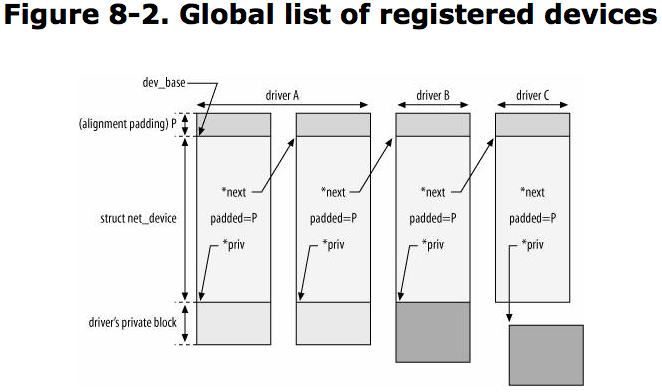
Organization of net_device Structures:
Device State:
net_device include:
- flags bitmap used to store different flags.
- reg_state device registration state
- state device state with regard to its queuing discipline.
Net Device Queuing Discipline State:
Each network device is assigned a queuing discipline, used by Traffic Control to implement its QoS mechanisms.
LINK_STATE_START
LINK_STATE_PRESENT
LINK_STATE_NOCARRIER
LINK_STATE_LINKWATCH_EVENT
LINK_STATE_XOFF
LINK_STATE_SHED
LINK_STATE_RX_SCHED
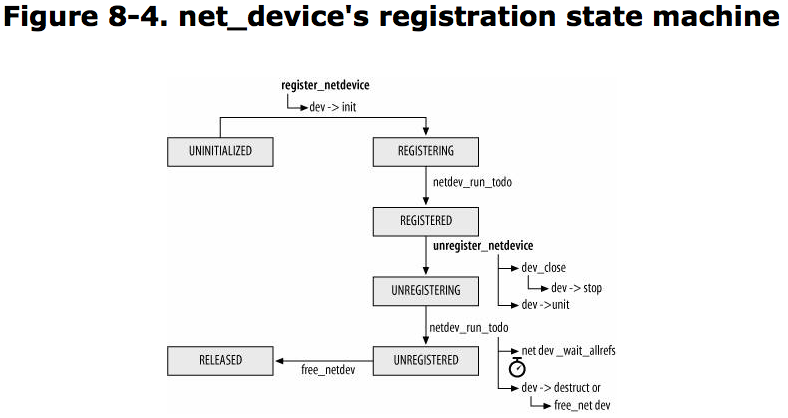
Net Device Registration State:
The state of a device with regard to its registration with the network stack is saved in reg_state field of the net_device structure.
NETREG_UNINITIALIZED
NETREG_REGISTERING
NETREG_REGISTERED
NETREG_UNREGISTERING
NETREG_UNREGISTERED
NETREG_RELEASED
Net Device register + unregister
Device Registration Status Notification:
Both kernel components and user-space applications are interested in knowing when a network device is registered, unregistered, goes down, or comes up.
netdev_chain: kernel components can register with this notification chain.
All the NETDEV_XXX events that are reported via neTDev_chain are listed in
Notification event list:
NETDEV_UP
NETDEV_GOING_DOWN
NETDEV_DOWN
NETDEV_REGISTER
NETDEV_UNREGISTER
NETDEV_REBOOT
NETDEV_CHANGEADDR
NETDEV_CHANGENAME
NETDEV_CHANGE
Quite a few kernel components register to netdev_chain List:
- Routing
- Firewall
- Protocol code
- Virtual device
- RTnetlink
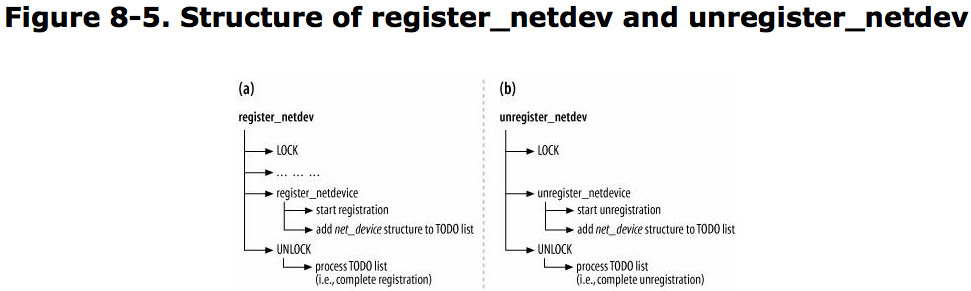
Enabling and Disabling a Network Device:
Virtual Devices:
The virtual devices need to be registered and enabled just like real ones, to be used.
register_netdevice/unregister_netdevice
Device initialization phases:
- Hardware initialization this is done by the device driver in cooperation with the generic bus layer(PCI or USB).
- Software initialization before the device can be used, it may need to provide some configuration parameters
- Feature initialization configure some options
net_device data structure include a set of function pointers, that kernel uses to interact with the device driver and special kernel features
Basic Goals of NIC Initialization:
establish device/kernel communication. such as:
- IRQ line the /proc/interrupts file can be used to view the status of the current assignments.
- I/O ports and memory registration map an area of device’s memory into system memory. I/O ports and memory are registered and released with request_region/release_region
Interaction Between Devices and Kernel:
nearly all devices interact with kernel in two ways:
- Polling driven on the kernel side, the kernel check device status at regular intervals.
- Interrupt driven on the device side, the device sends a hardware signal to kernel.
Hardware Interrupts:
every interrupt runs a function called an interrupt handler. IRQ are defined in kernel/irq/manage.c and are overridden by arch/XXX/kernel/irq.c.
NIC Inteerrupt Types:
- Reception of a frame
- Transmission failure
- DMA transfer has completed successfully
- Device has enough memory to handle a new transmission12345678910111213drivers/net/3c509.c:static intel3_start_xmit(struct sk_buff *skb, struct net_device *dev){... ... ...netif_stop_queue (dev);... ... ...if (inw(ioaddr + TX_FREE) > 1536)netif_start_queue(dev);elseoutw(SetTxThreshold + 1536, ioaddr + EL3_CMD);... ... ...}
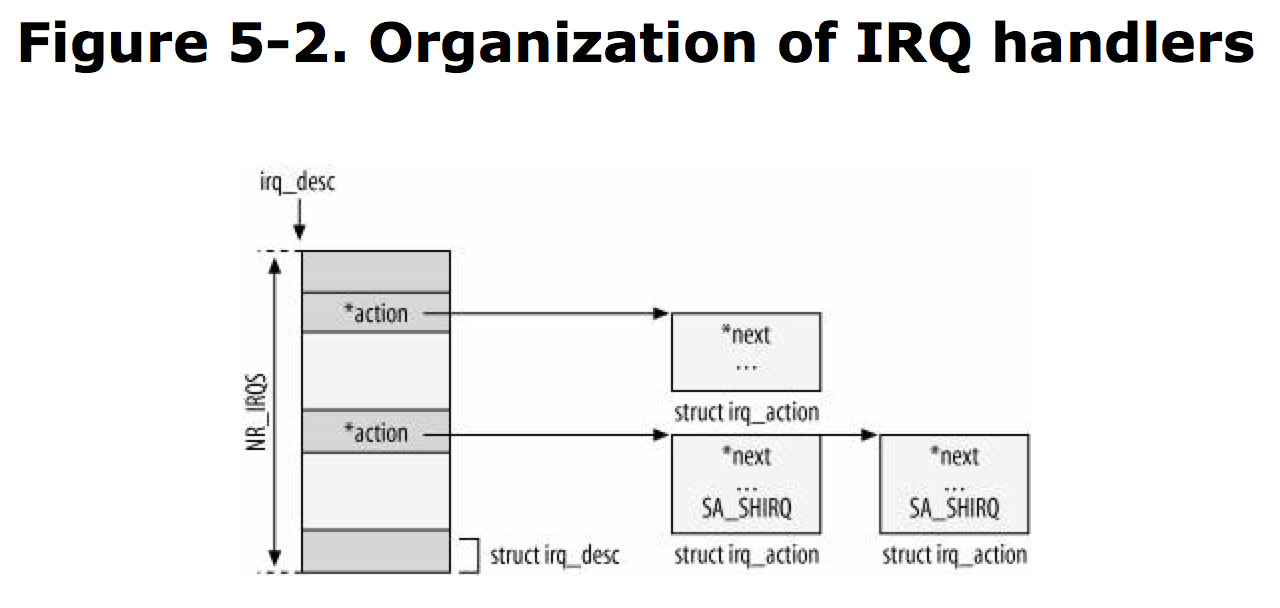
Organization of IRQs to handler mappings:
|
|